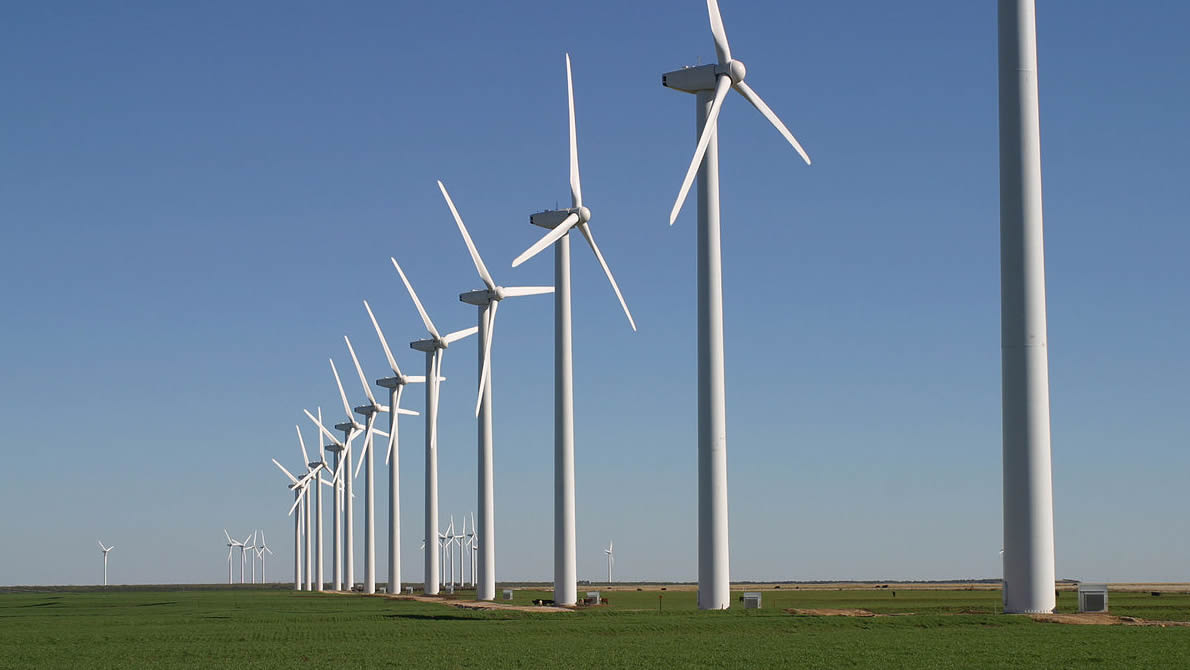
People think of wind as an energy source with few limits, offering an unending power source with distinct capacity advantages over sources that deplete, such as fossil fuel.
Yet, new research in mesoscale atmospheric modeling by lead author Amanda S. Adams of UNC Charlote and co-author David W. Keith of Harvard University, published Monday, Feb. 25 in the journal Environmental Research Letters, suggests that the power capacity of large-scale wind farms may have been significantly overestimated.
With large-scale wind farms, as many as hundreds of turbines mounted on tall towers and connected to the electrical grid capture the kinetic energy of the wind. Each wind turbine creates a “wind shadow” behind it, in which the turning blades slow the air. In an effort to reduce the impact of the wind shadows, wind farms space the turbines apart, while still locating as many turbines as they can on the land.
Current estimates of the global wind power resource over land range from 56 to 400 terawatts. Most of these estimates assume implicitly that the turbines extracting the wind energy have little impact on the atmosphere and, therefore, little effect on the energy production.
The new research says that scientists have underestimated the impact that large numbers of wind turbines have on energy production within large farms. Estimates of wind capacity that ignore the effect of wind turbine drag on local winds have assumed that wind power production of 2 and 4 watts per square meter could be sustained over large areas.
The new modeling results suggest that the generating capacity is more likely limited to about 1 watt per square meter at wind farms that are larger than 100 square kilometers.
“It’s easy to mistake the term renewable with the term unlimited when discussing energy,” said Adams, who is lead author. “Just because you can keep generating new energy from a source does not mean you can generate energy in an unlimited amount.”
The research suggests the potential for wind energy could be significantly less than previously thought.
“It’s important to take into account all factors impacting the wind energy, so we can assess the capacity of this critical power resource,” Adams said. “One of the inherent challenges is how harvesting the resource changes it, making it difficult to accurately calculate how much energy can be produced. The modeling we have done provides information that can help in the understanding of our ability to count on renewable energy sources.”
The research also considers the impact of wind energy production on temperatures and by extension possibly climate. Wind farms change the natural wind shear and produce various scales of turbulence. Higher potential temperatures are mixed downward due to this turbulence and result in low level warming, the research indicates.
“Our research suggests that how densely the turbines are placed affects not only energy production but also environmental impacts,” Adams said. “We see this impact on average temperatures not only at large-scale farms, but also in small-density wind farms. Some things to consider are the magnitude of temperature changes and also the size of the area affected. We think these findings indicate that additional research is needed in these areas.”
The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada funded the research.
Adams, an assistant professor of Geography & Earth Sciences in College of Liberal Arts & Sciences at UNC Charlotte, is lead author on the paper. Adams also is a faculty fellow with UNC Charlotte’s IDEAS (Infrastructure, Design, Environment & Sustainability) Center and is affiliated with the university’s Energy Production & Infrastructure Center (EPIC.) She is a member of the American Meteorological Society’s Energy Committee and a member of the Leadership Board of the Earth Science Women’s Network.
The co-author of the paper, Keith, is Gordon McKay Professor of Applied Physics at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Science and professor of public policy at Harvard Kennedy School.
Adams’ primary research interests focus on mesoscale phenomena, processes, and modeling with an emphasis on phenomena that involve boundary layer processes and/or topographic influences. In recent years, she and her research group at UNC Charlotte have focused on the link between small-scale processes and climate, particularly at the atmosphere and earth surface interface. Her research group concentrates primarily on question at the interface between energy, weather and climate.
Current questions her group is addressing include: How will large scale wind energy development impact the Great Plains low level jet? What are the meteorological conditions that lead to wind turbine icing? How does temperature variability in urban areas impact electricity demand? Can we quantify the risks of off shore wind turbines to hurricanes? The energy-related research that Adams’ group is conducting includes collaborations with San Diego Gas & Electric, Xcel Energy, and the Weather Underground.
Her primary teaching responsibility is for the Dynamic Meteorology sequence for the undergraduate Meteorology program. She also teaches undergraduate and graduate level classes on Mesoscale Meteorology, Mountain Meteorology and Snowpack Hydrology, Boundary Layer Meteorology, and Energy and Climate Change.